


 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The modulus operator works on integers (and integer expressions) and yields the remainder when the first operand is divided by the second. In Python, the modulus operator is a percent sign (%). The syntax is the same as for other operators:
>>> quotient = 7 / 3
>>> print quotient
2
>>> remainder = 7 % 3
>>> print remainder
1
So 7 divided by 3 is 2 with 1 left over.
The modulus operator turns out to be surprisingly useful. For
example, you can check whether one number is divisible by another if
x % y is zero, then x is divisible by y.
Also, you can extract the right-most digit or digits from a number. For example, x % 10 yields the right-most digit of x (in base 10). Similarly x % 100 yields the last two digits.
A boolean expression is an expression that is either true or false. In Python, an expression that is true has the value 1, and an expression that is false has the value 0.
The operator == compares two values and produces a boolean expression:
>>> 5 == 5
1
>>> 5 == 6
0
In the first statement, the two operands are equal, so the expression evaluates to 1 (true); in the second statement, 5 is not equal to 6, so we get 0 (false).
The == operator is one of the comparison operators; the others are:
x != y # x is not equal to y
x > y # x is greater than y
x < y # x is less than y
x >= y # x is greater than or equal to y
x <= y # x is less than or equal to y
Although these operations are probably familiar to you, the Python symbols are different from the mathematical symbols. A common error is to use a single equal sign (=) instead of a double equal sign (==). Remember that = is an assignment operator and == is a comparison operator. Also, there is no such thing as =< or =>.
There are three logical operators: and, or, and not. The semantics (meaning) of these operators is similar to their meaning in English. For example, x > 0 and x < 10 is true only if x is greater than 0 and less than 10.
n%2 == 0 or n%3 == 0 is true if either of the conditions is true, that is, if the number is divisible by 2 or 3.
Finally, the not operator negates a boolean expression, so not(x > y) is true if (x > y) is false, that is, if x is less than or equal to y.
Strictly speaking, the operands of the logical operators should be boolean expressions, but Python is not very strict. Any nonzero number is interpreted as "true."
>>> x = 5
>>> x and 1
1
>>> y = 0
>>> y and 1
0
In general, this sort of thing is not considered good style. If you want to compare a value to zero, you should do it explicitly.
In order to write useful programs, we almost always need the ability to check conditions and change the behavior of the program accordingly. Conditional statements give us this ability. The simplest form is the if statement:
if x > 0:
print "x is positive"
The boolean expression after the if statement is called the condition. If it is true, then the indented statement gets executed. If not, nothing happens.
Like other compound statements, the if statement is made up of a header and a block of statements:
HEADER:
FIRST STATEMENT
...
LAST STATEMENT
The header begins on a new line and ends with a colon (:). The indented statements that follow are called a block. The first unindented statement marks the end of the block. A statement block inside a compound statement is called the body of the statement.
There is no limit on the number of statements that can appear in the body of an if statement, but there has to be at least one. Occasionally, it is useful to have a body with no statements (usually as a place keeper for code you haven't written yet). In that case, you can use the pass statement, which does nothing.
A second form of the if statement is alternative execution, in which there are two possibilities and the condition determines which one gets executed. The syntax looks like this:
if x%2 == 0:
print x, "is even"
else:
print x, "is odd"
If the remainder when x is divided by 2 is 0, then we know that x is even, and the program displays a message to that effect. If the condition is false, the second set of statements is executed. Since the condition must be true or false, exactly one of the alternatives will be executed. The alternatives are called branches, because they are branches in the flow of execution.
As an aside, if you need to check the parity (evenness or oddness) of numbers often, you might "wrap" this code in a function:
def printParity(x):
if x%2 == 0:
print x, "is even"
else:
print x, "is odd"
For any value of x, printParity displays an appropriate message. When you call it, you can provide any integer expression as an argument.
>>> printParity(17)
>>> printParity(y+1)
Sometimes there are more than two possibilities and we need more than two branches. One way to express a computation like that is a chained conditional:
if x < y:
print x, "is less than", y
elif x > y:
print x, "is greater than", y
else:
print x, "and", y, "are equal"
elif is an abbreviation of "else if." Again, exactly one branch will be executed. There is no limit of the number of elif statements but only a single (and optional) else statement is allowed and it must be the last branch in the statement:
if choice == 'A':
functionA()
elif choice == 'B':
functionB()
elif choice == 'C':
functionC()
else:
print "Invalid choice."
Each condition is checked in order. If the first is false, the next is checked, and so on. If one of them is true, the corresponding branch executes, and the statement ends. Even if more than one condition is true, only the first true branch executes.
As an exercise, wrap these examples in functions called compare(x, y) and dispatch(choice).
One conditional can also be nested within another. We could have written the trichotomy example as follows:
if x == y:
print x, "and", y, "are equal"
else:
if x < y:
print x, "is less than", y
else:
print x, "is greater than", y
The outer conditional contains two branches. The first branch contains a simple output statement. The second branch contains another if statement, which has two branches of its own. Those two branches are both output statements, although they could have been conditional statements as well.
Although the indentation of the statements makes the structure apparent, nested conditionals become difficult to read very quickly. In general, it is a good idea to avoid them when you can.
Logical operators often provide a way to simplify nested conditional statements. For example, we can rewrite the following code using a single conditional:
if 0 < x:
if x < 10:
print "x is a positive single digit."
The print statement is executed only if we make it past both the conditionals, so we can use the and operator:
if 0 < x and x < 10:
print "x is a positive single digit."
These kinds of conditions are common, so Python provides an alternative syntax that is similar to mathematical notation:
if 0 < x < 10:
print "x is a positive single digit."
This condition is semantically the same as the compound boolean expression and the nested conditional.
The return statement allows you to terminate the execution of a function before you reach the end. One reason to use it is if you detect an error condition:
import math
def printLogarithm(x):
if x <= 0:
print "Positive numbers only, please."
return
result = math.log(x)
print "The log of x is", result
The function printLogarithm takes a parameter named x. The first thing it does is check whether x is less than or equal to 0, in which case it displays an error message and then uses return to exit the function. The flow of execution immediately returns to the caller, and the remaining lines of the function are not executed.
Remember that to use a function from the math module, you have to import it.
We mentioned that it is legal for one function to call another, and you have seen several examples of that. We neglected to mention that it is also legal for a function to call itself. It may not be obvious why that is a good thing, but it turns out to be one of the most magical and interesting things a program can do. For example, look at the following function:
def countdown(n):
if n == 0:
print "Blastoff!"
else:
print n
countdown(n-1)
countdown expects the parameter, n, to be a positive
integer. If n is 0, it outputs the word, "Blastoff!"
Otherwise, it outputs n and then calls a function named
countdown itself passing n-1 as an argument.
What happens if we call this function like this:
>>> countdown(3)
The execution of countdown begins with n=3, and since n is not 0, it outputs the value 3, and then calls itself...
The execution of countdown begins with n=2, and since n is not 0, it outputs the value 2, and then calls itself...The execution of countdown begins with n=1, and since n is not 0, it outputs the value 1, and then calls itself...The execution of countdown begins with n=0, and since n is 0, it outputs the word, "Blastoff!" and then returns.The countdown that got n=1 returns.
The countdown that got n=2 returns.
The countdown that got n=3 returns.
And then you're back in __main__ (what a trip). So, the total output looks like this:
3
2
1
Blastoff!
As a second example, look again at the functions newLine and threeLines:
def newline():
print
def threeLines():
newLine()
newLine()
newLine()
Although these work, they would not be much help if we wanted to output 2 newlines, or 106. A better alternative would be this:
def nLines(n):
if n > 0:
print
nLines(n-1)
This program is similar to countdown; as long as n is greater than 0, it outputs one newline and then calls itself to output n-1 additional newlines. Thus, the total number of newlines is 1 + (n - 1) which, if you do your algebra right, comes out to n.
The process of a function calling itself is recursion, and such functions are said to be recursive.
In Section 3.11, we used a stack diagram to represent the state of a program during a function call. The same kind of diagram can help interpret a recursive function.
Every time a function gets called, Python creates a new function frame, which contains the function's local variables and parameters. For a recursive function, there might be more than one frame on the stack at the same time.
This figure shows a stack diagram for countdown called with n = 3:
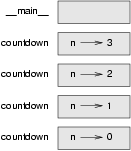
As usual, the top of the stack is the frame for __main__. It is empty because we did not create any variables in __main__ or pass any parameters to it.
The four countdown frames have different values for the parameter n. The bottom of the stack, where n=0, is called the base case. It does not make a recursive call, so there are no more frames.
As an exercise, draw a stack diagram for nLines called with n=4.
If a recursion never reaches a base case, it goes on making recursive calls forever, and the program never terminates. This is known as infinite recursion, and it is generally not considered a good idea. Here is a minimal program with an infinite recursion:
def recurse():
recurse()
In most programming environments, a program with infinite recursion does not really run forever. Python reports an error message when the maximum recursion depth is reached:
File "<stdin>", line 2, in recurse
(98 repetitions omitted)
File "<stdin>", line 2, in recurse
RuntimeError: Maximum recursion depth exceeded
This traceback is a little bigger than the one we saw in the previous chapter. When the error occurs, there are 100 recurse frames on the stack!
As an exercise, write a function with infinite recursion and run it in the Python interpreter.
The programs we have written so far are a bit rude in the sense that they accept no input from the user. They just do the same thing every time.
Python provides built-in functions that get input from the keyboard. The simplest is called raw_input. When this function is called, the program stops and waits for the user to type something. When the user presses Return or the Enter key, the program resumes and raw_input returns what the user typed as a string:
>>> input = raw_input ()
What are you waiting for?
>>> print input
What are you waiting for?
Before calling raw_input, it is a good idea to print a message telling the user what to input. This message is called a prompt. We can supply a prompt as an argument to raw_input:
>>> name = raw_input ("What...is your name? ")
What...is your name? Arthur, King of the Britons!
>>> print name
Arthur, King of the Britons!
If we expect the response to be an integer, we can use the input function which interprets the response as a Python value:
prompt = "What...is the airspeed velocity of an unladen swallow?\n"
speed = input(prompt)
If the user types a string of digits, it is converted to an integer and assigned to speed. Unfortunately, if the user types a character that is not a digit, the program crashes:
>>> speed = input (prompt)
What...is the airspeed velocity of an unladen swallow?
What do you mean, an African or a European swallow?
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
To avoid this kind of error, it is generally a good idea to use raw_input to get a string and then use conversion functions to convert to other types.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |